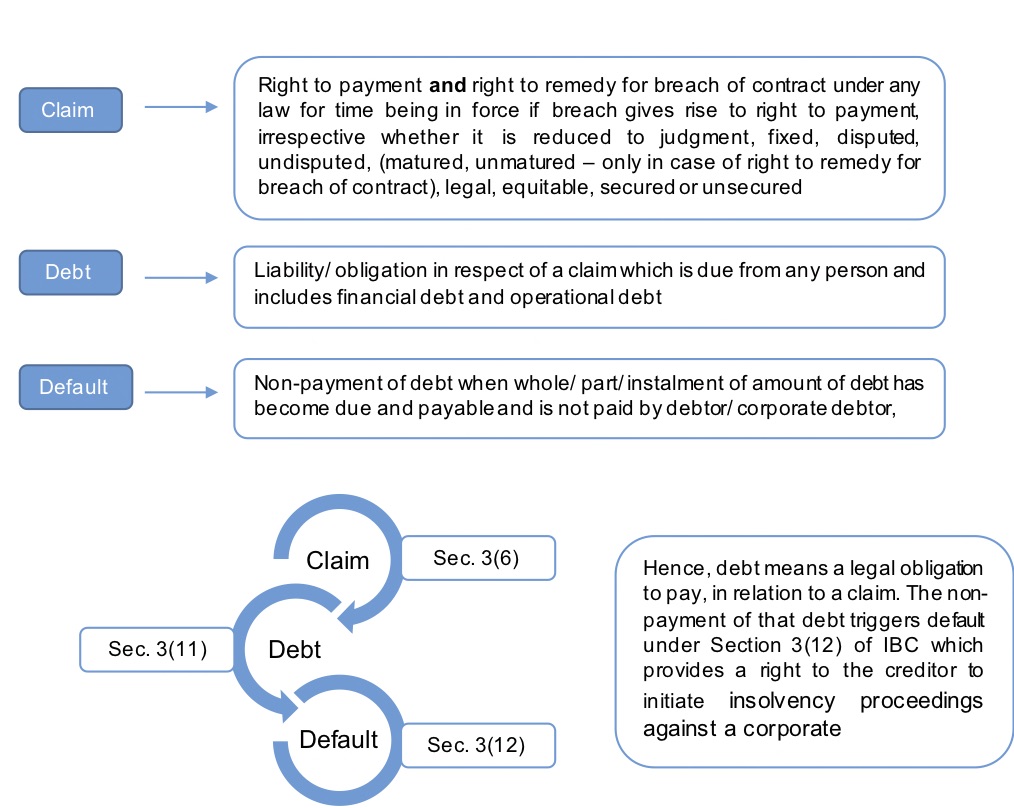
The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 (‘IBC’), as stated in the preamble of the code, has been enacted as a legislation for consolidating and amending the laws relating to reorganisation and insolvency resolution in a time-bound manner for maximization of value of assets , promote entrepreneurship, availability of credit including alteration in the order of priority of payment of government dues. The provisions of IBC have an overriding effect over other enactments in case of any inconsistency. To give teeth to the IBC, amendments have been made under several legislations including the Companies Act, Income Tax Act, The RDBFI Act, SARFAESI Act, etc.
Given this backdrop, it is relevant to examine the interplay of IBC vis-à-vis the Income Tax Act and its impact on the latter. This understanding assumes significance as it impacts the interests, rights, obligations and duties not only of the taxpayer and the income tax authorities, but also other stakeholders such as the creditors, resolution applicant, resolution professional, liquidator, etc.
Does the IBC prevail over tax laws?
The primary question-whether IBC prevails over the Income Tax Act can be analysed in light of S. 238 of IBC which states to the effect that provision of IBC overrides all other enactments to the extent inconsistent. The provision provides as under:
“The provisions of this Code shall have effect, notwithstanding anything inconsistent therewith contained in any other law for the time being in force or any instrument having effect by virtue of any such law.”
In this context, the overriding effect of IBC over the Income Tax Act has been examined by the Hon’ble Supreme Court in the case of Pr. Commissioner of Income Tax Vs. Monnet Ispat and Energy Ltd, wherein the court has ruled that S. 238 of IBC will override anything inconsistent contained in any other enactment, including the Income Tax Act. This has significant impact on regular tax matters as can be inferred from judicial development over the period.
Suspension of tax proceedings and institution of appeals during moratorium
The IBC provides for a period of moratorium from the date of admission of resolution application by the Adjudicating Authority i.e. the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT). The moratorium is declared u/s 14 of IBC which prohibits-
“the institution of suits or continuation of pending suits or proceedings against the corporate debtor including execution of any judgement, decree or order in any court of law, tribunal, arbitration panel or other authority”.
Such moratorium has effect till the completion of the corporate insolvency resolution process or approval of resolution plan or passing of order for liquidation of corporate debtor.
In context of tax laws, it merits consideration that the moratorium also applies to tax proceedings, appeals and litigations (pending or new) during the period. The position has been upheld by the Hon’ble Delhi High Court (affirmed by the Hon’ble Supreme Court) in PR. COMMISSIONER OF INCOME TAX-6, NEW DELH v. Pr. Commissioner of Income Tax Vs. Monnet Ispat and Energy Ltd.
It is however relevant to note that in certain cases, for instance, as was in the case of Deputy Commissioner of Income Tax Vs. Bhuvan Madan RP for Diamond Power Infrastructure Ltd. & Anr, considering the necessity of the assessment arising out of search proceedings and findings of irregularities by the Corporate Debtor (which may have led to huge tax demand), the prayer of the tax authorities was accepted to the extent of only conducting assessment. The continuation of proceedings was considered necessary to protect the interest of the exchequer. The NCLT however directed that tax authorities may file their claim as operational creditor with the resolution professional for examining the claim in accordance with the provisions of the code.
The short point being that tax proceedings including litigation before appellate forums would need to be kept in abeyance during the moratorium period. In certain cases, and as an exception to the general rule, continuation may be permitted subject to necessary direction by the NCLT. However, such proceedings cannot culminate in enforcing recovery of outstanding taxes during the moratorium period which can only be claimed in the manner prescribed for operational creditors.
Downward settlement of crystalized tax liability under resolution plan
One significant impact of IBC on income tax law is regarding the recovery of tax due. As part of the resolution process, the resolution applicant (for simplicity – the potential acquirer) is required to submit a resolution plan for the revival of the corporate debtor, which on approval by the NCLT is binding. The resolution plan provides for, amongst others, the payment of debts of operational creditors which cannot be less than the amount to be paid to such creditors in the event of a liquidation of the corporate debtor. In other words, the resolution plan would typically provide for a haircut of the outstanding dues towards various stakeholders including operational creditors and resultantly also the dues of the tax authorities (regarded as operational creditors).
The significance and magnitude of this can be judged from the facts in the case of Pr. Director General of Income Tax (Admn. & TPS) & Ors. Vs. Synergies Dooray Automative Ltd. & Ors. wherein NCLT (Hyderabad) approved the resolution plan under which the income tax liability/ demand in respect of the corporate debtor amounting to Rs. 338 Crores was settled for 1% of the ‘crystallized demand’ to a maximum of Rs.2.58 crores. In the appeal filed against the order of the NCLT, The NCLAT (Delhi) ruled that statuary dues are operational creditors and equated with similarly situated ‘operational creditors’. There was accordingly no infirmity in settlement of tax dues pursuant to approved resolution plan thereby approving a significant write-off of statutory dues.
Tax during liquidation
Another interesting issue recently arose in the case of LML Limited Vs. Office of Commissioner of Income Tax, Mumbai [NCLT Allahabad Bench] regarding payment of capital gain tax on sale of assets of the corporate debtor in liquidation. The question was whether such capital gain tax would form part of ‘liquidation expense” and hence payable in priority of other claims such as of secured creditors & workmen compensation etc, as per waterfall mechanism u/s 53 of IBC. The NCLT ruled that capital gain tax would not form part of liquidation cost and hence can only be recovered in the order of priority specified u/s 53. The NCLT took note of the amendment in section 178(6) of the Income Tax Act providing overriding effect of IBC and also S. 238 of the IBC ruling that the provision of the code shall have an overriding effect on any other enactment. While one may debate whether capital gain liability arising in the circumstances is ‘liquidation expense’ or not, however if the determination is held to be correct, there can be significant impact on recovery of taxes by the exchequer consequent to overriding effect of IBC.
In somewhat relatable situation, in Om Prakash Agarwal Vs. Chief Commissioner Of Income Tax (TDS) & Anr., the question arose with respect to applicability of TDS on sale proceeds received by the liquidator under section 194 (IA) [TDS of 1% applicable on transferor of immoveable property]. The Principle Bench, NCLT held in favour of the tax authorities observing that the overriding effect u/s 238 is applicable to the issues between the creditor and the debtor but not to TDS deductions. It held that deduction of TDS does not tantamount to payment of government dues in priority to other creditors since it is not a tax demand for realisation of tax dues. It observed that the liquidator is not asked to pay TDS and it is the duty of the purchaser to credit TDS to the account of income tax authorities.
In conclusion, the above highlights some of the nuances of law and the issues involved relating to aspects of tax proceedings, recovery of tax, tax deduction, attachment of assets, etc. Ordinarily, the conventional wisdom on tax laws would generally lead one to assume the overarching dominance of the tax laws and administration against all others claims and proceedings. Given much has changed with the advent of IBC, an isolated analysis of the income tax law will be entirely inadequate while dealing with tax matters. Both legislations prescribe severe implications in case of defaults under either law making it that much more relevant to examine the tax laws through the prism of IBC.
Contributed by Yatin Sharma.
Yatin can be reached at yatin.sharma@aureuslaw.com.